Forward Education Trust is made up of a group of Academies in Birmingham. I am proud to lead and work closely with our talented senior leaders, dedicated school and Trust staff and skilled. Unipolar transistor b. Bipolar transistor c. Tri-polar transistor d. None of these 3. An FET is characterised by a. None of these 4. The input impedance of an FET is of the order of a. Hundreds of mega ohm c.
FET-1501-A MONTGOMERY COUNTY, MARYLAND DIVISION OF TREASURY – EXCISE TAX UNIT 255 Rockville Pike, Suite L-15 Rockville, Maryland 20850 Phone (240) 777-0311 FUEL-ENERGY TAX RETURN For Use by Dealers of Fuel Oil, L.P. Gas, Coal and Steam Name IMPORTANT Address This return must be filed on or before the last day of the month immediately. In this video, the brief introduction to the Field Effect Transistor (FET) has been given and the different types of FETs are discussed. By watching this vid.
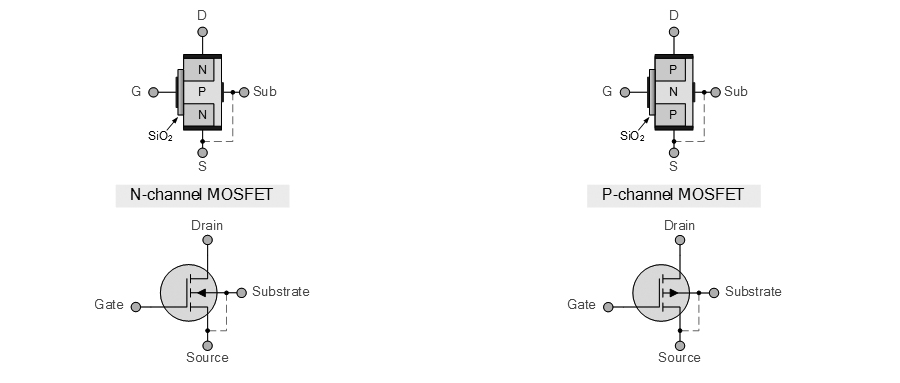
A FET amplifier is an amplifier that uses one or more field-effect transistors (FETs). The most common type of FET amplifier is the MOSFET amplifier, which uses metal–oxide–semiconductor FETs (MOSFETs). The main advantage of a FET used for amplification is that it has very high input impedance and low output impedance.
In detail[edit]
The transconductance is given by

On rearranging, we get
Equivalent circuit[edit]
The internal resistance Rgs, between gate and source appears between drain and source. Rds is internal resistance between drain and source.As Rgs is very high, it is taken to be infinite and Rds is neglected.[1]
Voltage gain[edit]
For ideal FET equivalent circuit, voltage gain is given by,
From the equivalent circuit,
and from the definition of transconductance,
we get
Types of FET amplifiers[edit]

There are three types of FET amplifiers: which terminal is the common input and output? (This is similar to a bipolar junction transistor (BJT) amplifier.)
Common gate amplifier[edit]
The gate is common to both input and output.
Common source amplifier[edit]
The source is common to both input and output.
Common drain amplifier[edit]
The drain is common to both input and output. It is also known as a 'source follower'.[2]
History[edit]
The basic principle of the field-effect transistor (FET) amplifier was first proposed by Austro-Hungarian physicist Julius Edgar Lilienfeld in 1925.[3] However, his early FET concept was not a practical design.[4] The FET concept was later also theorized by Oskar Heil in the 1930s and William Shockley in the 1940s,[5] but there was no working practical FET built at the time.[4]
MOSFET amplifier[edit]
A breakthrough came with the work of Egyptian engineer Mohamed M. Atalla in the late 1950s.[6] He developed the method of surface passivation, which later became critical to the semiconductor industry as it made possible the mass-production of siliconsemiconductor technology, such as integrated circuit (IC) chips.[7][4][8] For the surface passivation process, he developed the method of thermal oxidation, which was a breakthrough in silicon semiconductor technology.[9] The surface passivation method was presented by Atalla in 1957.[10] Building on the surface passivation method, Atalla developed the metal–oxide–semiconductor (MOS) process,[7] with the use of thermally oxidized silicon.[11][12] He proposed that the MOS process could be used to build the first working silicon FET, which he began working on building with the help of Korean recruit Dawon Kahng.[7]
The MOS field-effect transistor (MOSFET) amplifier was invented by Mohamed Atalla and Dawon Kahng in 1959.[5] They fabricated the device in November 1959,[13] and presented it as the 'silicon–silicon dioxide field induced surface device' in early 1960,[14] at the Solid-State Device Conference held at Carnegie Mellon University.[15] The device is covered by two patents, each filed separately by Atalla and Kahng in March 1960.[16][17]

Federal Excise Tax On Trucks
See also[edit]
References[edit]
- ^ abThomas L. Floyd (2011). Electronic Devices. Dorling Kinersley (India) Pvt. Ltd., licensees of Pearson Education in South Asia. p. 252. ISBN978-81-7758-643-5.
- ^Allen Mottershead (2003). Electronic Devices and circuits. Prentice-Hall of India, New Delhi-110001. ISBN81-203-0124-2.
- ^Lilienfeld, Julius Edgar (1926-10-08) 'Method and apparatus for controlling electric currents' U.S. Patent 1745175A
- ^ abc'Dawon Kahng'. National Inventors Hall of Fame. Retrieved 27 June 2019.CS1 maint: discouraged parameter (link)
- ^ ab'1960: Metal Oxide Semiconductor (MOS) Transistor Demonstrated'. The Silicon Engine: A Timeline of Semiconductors in Computers. Computer History Museum. Retrieved August 31, 2019.CS1 maint: discouraged parameter (link)
- ^Puers, Robert; Baldi, Livio; Voorde, Marcel Van de; Nooten, Sebastiaan E. van (2017). Nanoelectronics: Materials, Devices, Applications, 2 Volumes. John Wiley & Sons. p. 14. ISBN9783527340538.
- ^ abc'Martin (John) M. Atalla'. National Inventors Hall of Fame. 2009. Retrieved 21 June 2013.CS1 maint: discouraged parameter (link)
- ^Lojek, Bo (2007). History of Semiconductor Engineering. Springer Science & Business Media. pp. 321–3. ISBN9783540342588.
- ^Huff, Howard (2005). High Dielectric Constant Materials: VLSI MOSFET Applications. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 34. ISBN9783540210818.
- ^Lojek, Bo (2007). History of Semiconductor Engineering. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 120. ISBN9783540342588.
- ^Deal, Bruce E. (1998). 'Highlights Of Silicon Thermal Oxidation Technology'. Silicon materials science and technology. The Electrochemical Society. p. 183. ISBN9781566771931.
- ^U.S. Patent 2,953,486
- ^Bassett, Ross Knox (2007). To the Digital Age: Research Labs, Start-up Companies, and the Rise of MOS Technology. Johns Hopkins University Press. p. 22. ISBN9780801886393.
- ^Atalla, M.; Kahng, D. (1960). 'Silicon–silicon dioxide field induced surface devices'. IRE-AIEE Solid State Device Research Conference. Carnegie Mellon University Press.
- ^'Oral-History: Goldey, Hittinger and Tanenbaum'. Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers. 25 September 2008. Retrieved 22 August 2019.CS1 maint: discouraged parameter (link)
- ^U.S. Patent 3,206,670 (1960)
- ^U.S. Patent 3,102,230 (1960)
How is FET a voltage controlled device?
the voltage applied between the gate and the source controls the drain current (id). which means you use the voltage to control the output current. therefore, fet is a voltage controlled device.
just explained because it consumes very little power to operate. it relies on the voltage differential to create a field effect necessary for its operation (hence the field effect transistor name). the amplitude of the voltage differential dictates the operating speed of the device.
A FET is voltage controlled device by virtue of the fact that current flow between the Drain and the Source is controlled by the voltage at the Gate in reference to the Source (Vgs).
a fet is controlled by a voltage at the terminal of the gate and, because of the very high grid impedance, flows in or out of the gate. compare to a bipolar transistor in the active state which is controlled by the current flowing from the base to the emitter, which allows to obtain a collector-emitter current proportional to the base-emitter current.
a fet is a voltage-controlled device because the current between the drain and the source is controlled by the voltage at the gate with reference to the source (vgs).
This contrasts with the current controlled bjt because the current flow between the collector and the emitter is controlled by the current flowing through the base.
Fet Is A Noun
why is a FET voltage controlled device?
Fet Is A Symbol
The most common type of fet is a type of insulated door. since the door is isolated from the drain and the source, no current can cross it (or very little, in practice). the fet has no choice: it can not be controlled by the current, it must be controlled by the electrostatic field created by the voltage on its grid. (hence its name: field effect transistor.)
or something like that!
Sugar sugargamefort. To be short and simple:
You vary the voltage at the terminal, you get a constant current at the output. this is because the gate voltage is used to control channel resistance or pinch condition.
While a transistor is a current-controlled device because the base current is used to control the output collector current (taking into account the configuration of the common emitter).
in practical cases, the mosfet is better than the fet (the effects of ionization in the fet make it unfit for use in practical circuits). that’s why we’ve installed a layer of metal oxide on the fet to improve its applications.
Feet Is A Yard
For more detailed explanations, study the output response graphs of fet and compare them with those of mosfet.
jfet is a voltage-controlled device because the input signal is applied to the reverse-biased pn junction (source gate), which allows only a leakage current (in nano amps). the input bias current is negligible, the voltage having a dominant effect (very high impedance of 100 megohms). the output current flows from the source to the drain; the variation of the gate voltage controls the drain current. Instrumentation amplifiers
jfet are used to amplify thermocouple signals in the microvolt range since virtually no bias current is drawn from the sensor.

by comparing bjt, it uses a live-biased pn junction inrush current in a range from micro to milliamps, resulting in low input impedance. Here, the change of the base current controls the greatest variation of the current of the collector. therefore, bjt is a current controlled apparatus.
it can be noted that in the two amplifiers bjt jfet, the voltage signals are given as input.
Which device is a voltage controlled device?

